Business process improvement sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail with American high school hip style and brimming with originality from the outset. From defining the concept to exploring methodologies and tools, get ready to dive into the world of optimizing business processes.
Introduction to Business Process Improvement
Yo, listen up! Business process improvement is all about making those workflows smoother and more efficient. It’s like giving your business a turbo boost to get things done faster and better.
Optimizing business processes is crucial because it helps cut down on wasted time, resources, and money. It’s all about streamlining operations and eliminating any bottlenecks that might be holding your business back.
Examples of Successful Business Process Improvement Initiatives
- One dope example is how Amazon revolutionized their fulfillment process with robots and automation. They slashed delivery times and improved customer satisfaction big time.
- Another lit example is how Toyota implemented the Toyota Production System, which focused on continuous improvement in manufacturing processes. This led to huge cost savings and quality improvements.
- And let’s not forget about how Starbucks used mobile ordering to speed up their coffee-making process and reduce wait times for customers. It’s all about that hustle!
Benefits of Business Process Improvement
Implementing process improvement strategies can offer numerous advantages to businesses. By optimizing processes, companies can streamline operations, reduce waste, and enhance overall efficiency. This can lead to cost savings, improved quality, and increased customer satisfaction.
Gaining a Competitive Edge
One of the key benefits of business process improvement is the ability for organizations to gain a competitive edge in the market. By continuously refining and enhancing their processes, businesses can adapt more quickly to changing market conditions, customer demands, and technological advancements. This agility allows companies to stay ahead of the competition and drive innovation in their industry.
Real-world Cost Savings, Business process improvement
There are several real-world instances where process improvement has led to significant cost savings for businesses. For example, a manufacturing company implemented a lean production system that reduced waste and improved efficiency, resulting in a 20% decrease in production costs. Similarly, a retail chain optimized its supply chain processes, leading to a 15% reduction in inventory holding costs. These examples demonstrate how process improvement can have a direct impact on the bottom line and contribute to long-term success.
Common Methodologies for Business Process Improvement
In the realm of business process improvement, there are several popular methodologies that organizations often turn to in order to streamline their operations and enhance efficiency. These methodologies, such as Six Sigma, Lean Management, and Kaizen, each have their own set of key principles and approaches that guide the improvement process.
Six Sigma
Six Sigma is a data-driven methodology that focuses on eliminating defects and variations in processes to achieve near-perfect results. The key principles of Six Sigma include defining, measuring, analyzing, improving, and controlling processes to ensure consistent quality and efficiency. By using statistical tools and techniques, organizations can identify and address root causes of problems to enhance overall performance.
Lean Management
Lean Management, inspired by the Toyota Production System, aims to minimize waste and maximize value for the customer. The key principles of Lean Management include identifying value from the customer’s perspective, mapping the value stream, creating flow, establishing pull, and continuously improving processes. By eliminating waste and optimizing resources, organizations can deliver products and services more efficiently and effectively.
Kaizen
Kaizen, which means “continuous improvement” in Japanese, focuses on making small, incremental changes to processes on a regular basis. The key principles of Kaizen include standardizing processes, involving employees at all levels, seeking input from frontline workers, and fostering a culture of continuous improvement. By encouraging employees to identify and implement improvements, organizations can achieve sustainable growth and innovation.
When comparing and contrasting these different methodologies, it is essential to consider the specific goals and objectives of the organization, as well as the nature of the processes being improved. While Six Sigma emphasizes data-driven decision-making and defect reduction, Lean Management focuses on waste elimination and value creation. On the other hand, Kaizen places a strong emphasis on employee involvement and continuous improvement at all levels of the organization. By understanding the unique strengths and principles of each methodology, organizations can choose the most suitable approach to drive business process improvement and achieve sustainable success.
Tools and Technologies for Business Process Improvement
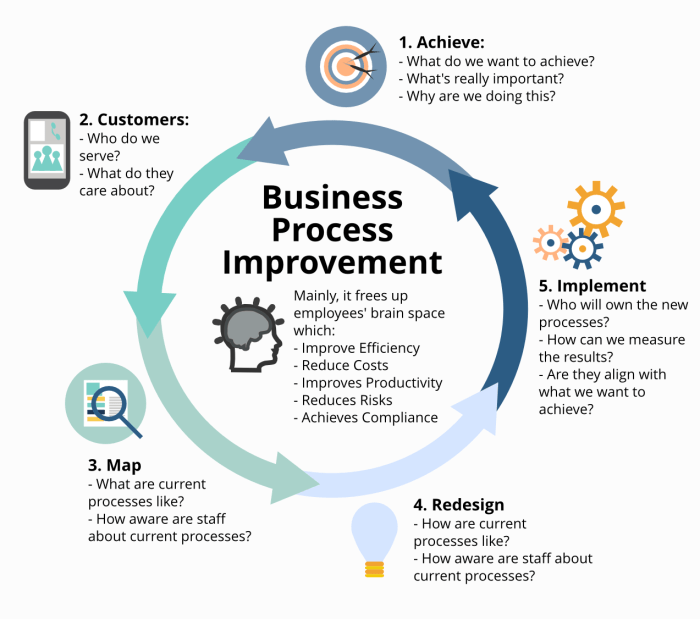
In order to enhance business process efficiency, various tools and technologies can be utilized to streamline processes and drive continuous improvement.
Process Mapping Software
- Process mapping software allows businesses to visually represent their workflows, identify bottlenecks, and optimize processes for maximum efficiency.
- By creating detailed process maps, organizations can gain insights into their current processes and make informed decisions on where improvements are needed.
- Tools like Microsoft Visio, Lucidchart, and Bizagi are commonly used for process mapping.
Workflow Automation Systems
- Workflow automation systems help automate repetitive tasks, reduce manual errors, and increase productivity by streamlining the flow of work.
- These systems can automate approvals, notifications, and data entry processes, leading to faster turnaround times and cost savings.
- Popular workflow automation tools include Kissflow, Nintex, and Zapier.
Data Analytics Tools
- Data analytics tools enable organizations to analyze large datasets, identify patterns, and make data-driven decisions to improve processes.
- By leveraging data analytics, businesses can optimize processes, forecast trends, and enhance overall operational efficiency.
- Tools like Tableau, Power BI, and Google Analytics are commonly used for data analytics in business process improvement.
Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
- RPA technology allows organizations to automate repetitive tasks, mimic human actions, and increase the speed and accuracy of business processes.
- By implementing RPA, businesses can reduce manual effort, eliminate errors, and free up employees to focus on more strategic tasks.
- Popular RPA tools include UiPath, Automation Anywhere, and Blue Prism.
Steps to Implement Business Process Improvement
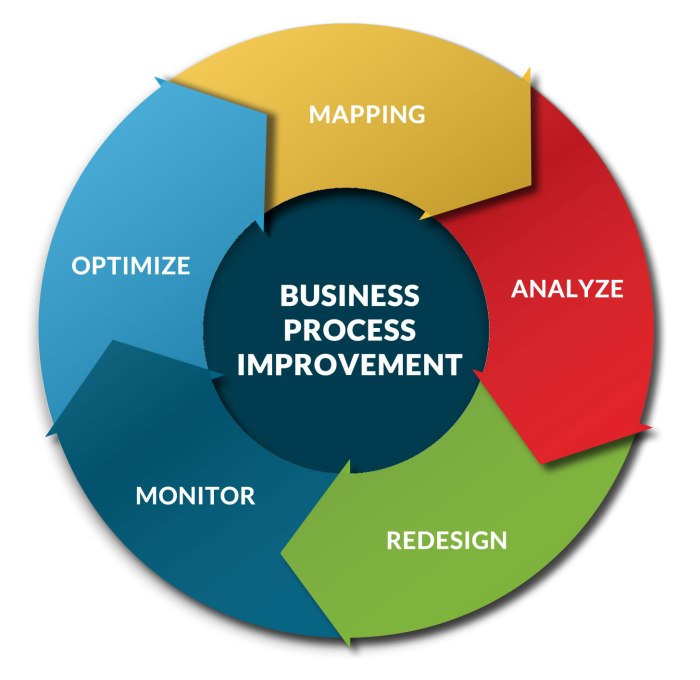
Implementing business process improvement can be a game-changer for organizations looking to streamline operations and increase efficiency. Here is a step-by-step guide to help businesses kickstart their process improvement initiatives.
1. Identify Areas for Improvement
- Conduct a thorough analysis of current processes to pinpoint bottlenecks, inefficiencies, and areas with high error rates.
- Solicit feedback from employees at all levels to gain insights into pain points and areas that could benefit from optimization.
- Utilize data analytics and performance metrics to identify trends and patterns that indicate areas for improvement.
2. Set Clear Objectives and Goals
- Define specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) objectives for the process improvement initiative.
- Align goals with overall organizational strategy and ensure they are communicated effectively to all stakeholders.
- Establish key performance indicators (KPIs) to track progress and measure the impact of the improvements.
3. Develop an Action Plan
- Break down the improvement process into actionable steps with clear timelines and responsibilities assigned to individuals or teams.
- Create a roadmap outlining the sequence of activities, milestones, and deadlines to ensure a structured approach to implementation.
- Allocate resources, budget, and technology required to support the implementation of the action plan.
4. Implement Changes and Monitor Progress
- Execute the action plan according to the defined timeline, making necessary adjustments along the way based on feedback and performance metrics.
- Regularly monitor progress against KPIs and evaluate the effectiveness of the implemented changes.
- Engage employees in the process and encourage feedback to ensure continuous improvement and sustainable results.
5. Evaluate Results and Continuously Improve
- Conduct a thorough assessment of the outcomes achieved through the process improvement initiative, comparing against initial objectives and goals.
- Identify successes, challenges, and areas for further enhancement to inform future improvement efforts.
- Establish a culture of continuous improvement within the organization to drive ongoing optimization and innovation.